Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Thyroid
- Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Thyroid Cancers: A Review of Current Practice Guidelines
- Min Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ji Ye Lee, Ji-hoon Kim, Kyungsik Kim, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):47-60. Published online February 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1937

- 1,897 View
- 173 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The indolent nature and favorable outcomes associated with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma have prompted numerous prospective studies on active surveillance (AS) and its adoption as an alternative to immediate surgery in managing low-risk thyroid cancer. This article reviews the current status of AS, as outlined in various international practice guidelines. AS is typically recommended for tumors that measure 1 cm or less in diameter and do not exhibit aggressive subtypes on cytology, extrathyroidal extension, lymph node metastasis, or distant metastasis. To determine the most appropriate candidates for AS, factors such as tumor size, location, multiplicity, and ultrasound findings are considered, along with patient characteristics like medical condition, age, and family history. Moreover, shared decision-making, which includes patient-reported outcomes such as quality of life and cost-effectiveness, is essential. During AS, patients undergo regular ultrasound examinations to monitor for signs of disease progression, including tumor growth, extrathyroidal extension, or lymph node metastasis. In conclusion, while AS is a feasible and reliable approach for managing lowrisk thyroid cancer, it requires careful patient selection, effective communication for shared decision-making, standardized follow-up protocols, and a clear definition of disease progression.

- Thyroid
- A Narrative Review of the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guideline for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
- Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park, Chan Kwon Jung, Dong Gyu Na
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):61-72. Published online February 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1938

- 1,506 View
- 95 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The 2023 Korean Thyroid Association (KTA) Management Guideline for Patients with Thyroid Nodules constitute an update of the 2016 KTA guideline for thyroid nodules and cancers that focuses specifically on nodules. The 2023 guideline aim to offer updated guidance based on new evidence that reflects the changes in clinical practice since the 2016 KTA guideline. To update the 2023 guideline, a comprehensive literature search was conducted from January 2022 to May 2022. The literature search included studies, reviews, and other evidence involving human subjects that were published in English in MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, and other relevant databases. Additional significant clinical trials and research studies published up to April 2023 were also reviewed. The limitations of the current evidence are discussed, and suggestions for areas in need of further research are identified. The purpose of this review is to provide a summary of the 2023 KTA guideline for the management of thyroid nodules released in May 2023 and to give a balanced insight with comparison of recent guidelines from other societies.

Original Articles
- Thyroid
- Hashimoto Thyroiditis and Mortality in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The National Epidemiologic Survey of Thyroid Cancer in Korea and Meta-Analysis
- Injung Yang, Jae Myung Yu, Hye Soo Chung, Yoon Jung Kim, Yong Kyun Roh, Min Kyu Choi, Sung-ho Park, Young Joo Park, Shinje Moon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):140-151. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1748
- 1,003 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
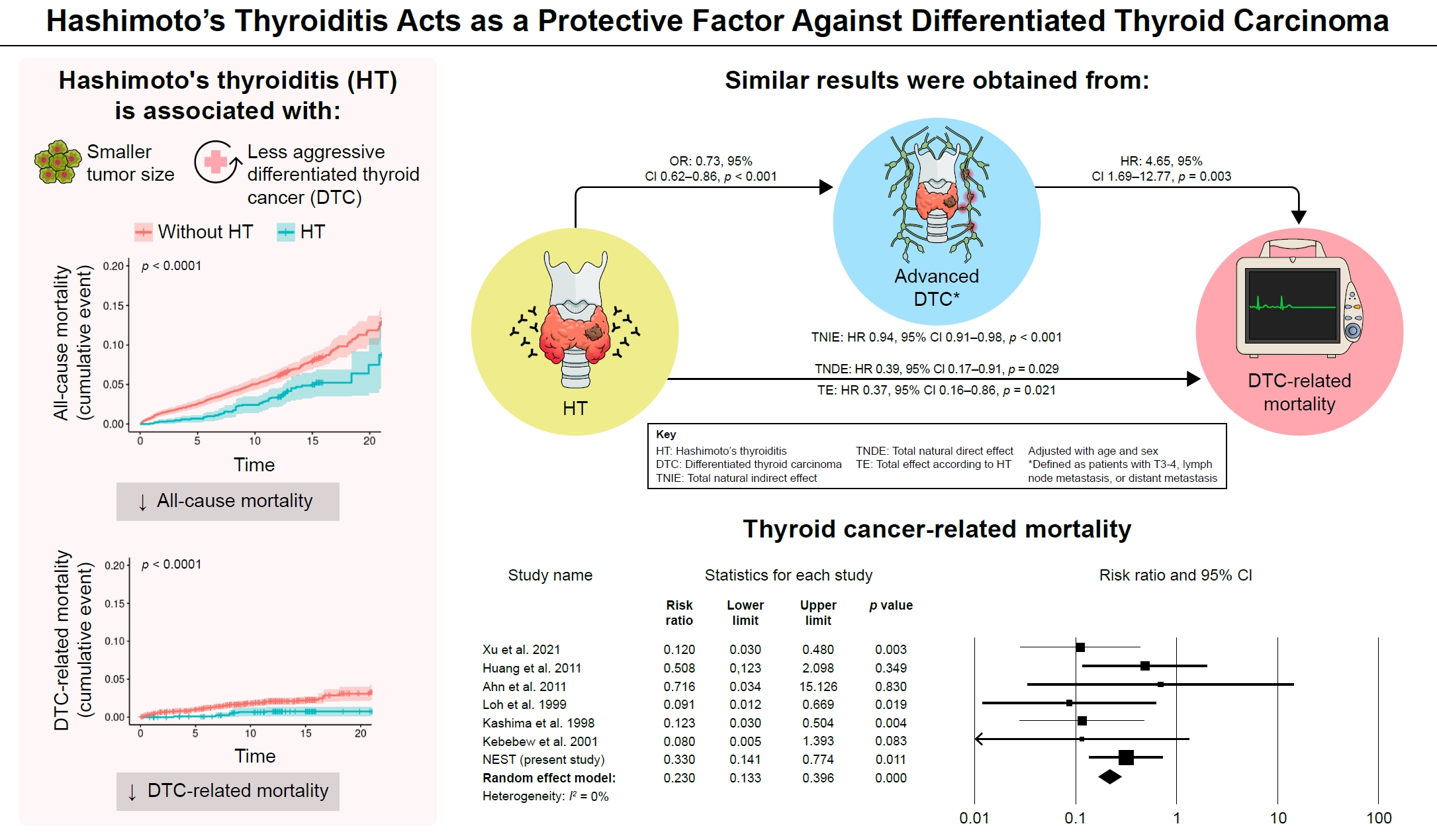
ePub - Background
Many studies have shown that Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT) acts as a protective factor in differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC), but little is known about its effects on mortality. Therefore, this study was performed to reveal the prognosis of HT on mortality in patients with DTC.
Methods
This study included two types of research results: retrospective cohort study using the National Epidemiologic Survey of Thyroid cancer (NEST) in Korea and meta-analysis study with the NEST data and eight selected studies.
Results
Of the 4,398 patients with DTC in NEST, 341 patients (7.8%) died during the median follow-up period of 15 years (interquartile range, 12.3 to 15.6). Of these, 91 deaths (2.1%) were related to DTC. HT was associated with a smaller tumor size and less aggressive DTC. In Cox regression analysis after adjusting for age and sex, patients with HT showed a significantly lower risk of all-cause death (hazard ratio [HR], 0.71; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.52 to 0.96) and DTC-related death (HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.14 to 0.77). The analysis with inverse probability of treatment weight data adjusted for age, sex, and year of thyroid cancer registration showed similar association. The meta-analysis showed that patients with HT showed a lower risk of all-cause mortality (risk ratio [RR], 0.24; 95% CI, 0.13 to 0.47) and thyroid cancer-related mortality (RR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.13 to 0.40) in comparison with patients without HT.
Conclusion
This study showed that DTC co-presenting with HT is associated with a low risk of advanced DTC and presents a low risk for all-cause and DTC-related death.

- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
- Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):436-444. Published online July 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1684
- 1,806 View
- 127 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
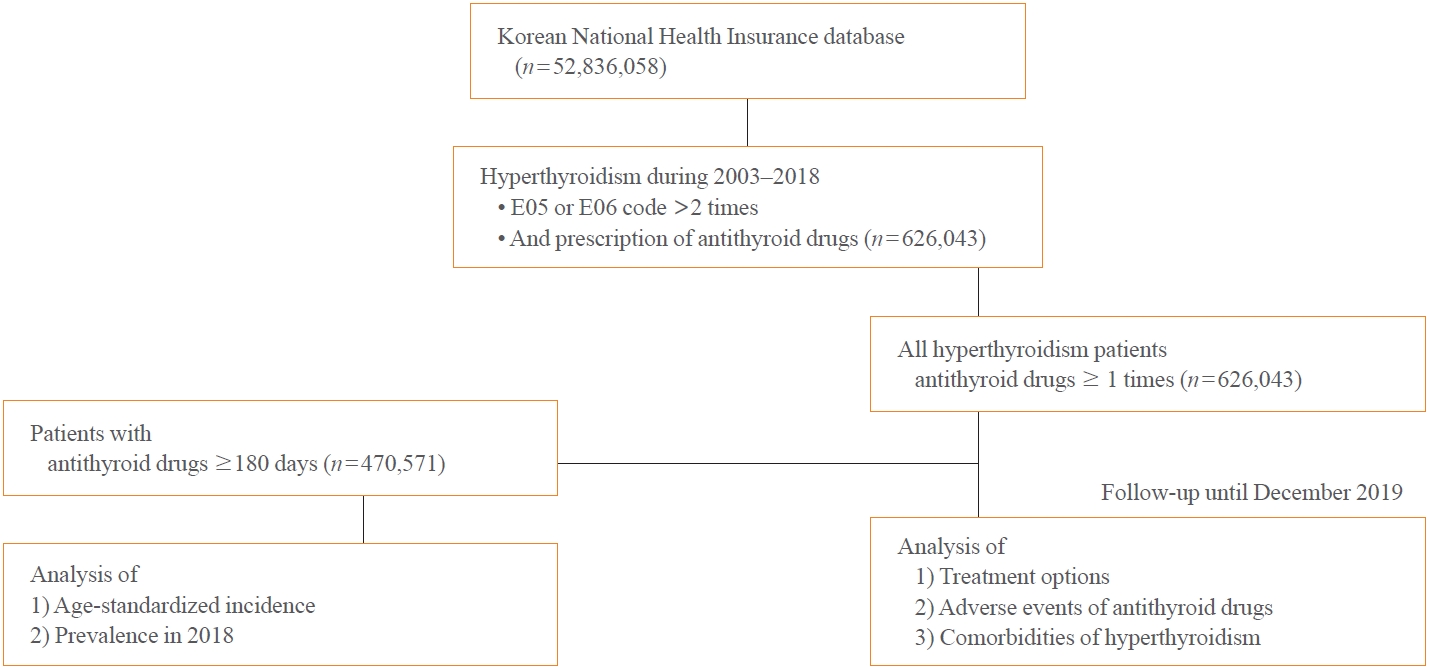
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the changes of incidence and treatment of choice for hyperthyroidism from 2003 to 2018 and explore the treatment-related complications and concomitant comorbidities in South Korea using data from the National Health Insurance Service.
Methods
This is a retrospective observational study. Hyperthyroidism was defined as a case having two or more diagnostic codes of thyrotoxicosis, with antithyroid drug intake for more than 6 months.
Results
The average age-standardized incidence of hyperthyroidism from 2003 to 2018 was 42.23 and 105.13 per 100,000 men and women, respectively. In 2003 to 2004, hyperthyroidism was most often diagnosed in patients in their 50s, but in 2017 to 2018, people were most often diagnosed in their 60s. During the entire period, about 93.7% of hyperthyroidism patients were prescribed with antithyroid drugs, and meanwhile, the annual rates of ablation therapy decrease from 7.68% in 2008 to 4.56% in 2018. Antithyroid drug-related adverse events, mainly agranulocytosis and acute hepatitis, as well as complications of hyperthyroidism such as atrial fibrillation or flutter, osteoporosis, and fractures, occurred more often in younger patients.
Conclusion
In Korea, hyperthyroidism occurred about 2.5 times more in women than in men, and antithyroid drugs were most preferred as the first-line treatment. Compared to the general population, hyperthyroid patients may have a higher risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter, osteoporosis, and fractures at a younger age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Is Thyroid Dysfunction Associated with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms? A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study from Korea
Hyeree Park, Sun Wook Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim, Aesun Shin, Won-Sang Cho
Thyroid®.2023; 33(12): 1483. CrossRef
- Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients

- Thyroid
Thyroid Cancer Screening - Survival Comparison of Incidentally Found versus Clinically Detected Thyroid Cancers: An Analysis of a Nationwide Cohort Study
- Shinje Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hoonsung Choi, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):81-92. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1668

- 1,726 View
- 154 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The true benefit of thyroid cancer screening is incompletely understood. This study investigated the impact of ultrasound screening on thyroid cancer outcomes through a comparison with symptomatic thyroid cancer using data from a nationwide cohort study in Korea.
Methods
Cox regression analysis was performed to assess the hazard ratios (HRs) for all-cause and thyroid cancer-specific mortality. Considering the possible bias arising from age, sex, year of thyroid cancer registration, and confounding factors for mortality (including smoking/drinking status, diabetes, and hypertension), all analyses were conducted with stabilized inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) according to the route of detection.
Results
Of 5,796 patients with thyroid cancer, 4,145 were included and 1,651 were excluded due to insufficient data. In comparison with the screening group, the clinical suspicion group was associated with large tumors (17.2±14.6 mm vs. 10.4±7.9 mm), advanced T stage (3–4) (odds ratio [OR], 1.24; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09 to 1.41), extrathyroidal extension (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.32), and advanced stage (III–IV) (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.00 to 1.35). In IPTW-adjusted Cox regression analysis, the clinical suspicion group had significantly higher risks of all-cause mortality (HR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.14 to 1.80) and thyroid cancer-specific mortality (HR, 3.07; 95% CI, 1.77 to 5.29). Mediation analysis showed that the presence of thyroid-specific symptoms was directly associated with a higher risk of cancer-specific mortality. Thyroid-specific symptoms also indirectly affected thyroid cancer-specific mortality, mediated by tumor size and advanced clinicopathologic status.
Conclusion
Our findings provide important evidence for the survival benefit of early detection of thyroid cancer compared to symptomatic thyroid cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Characteristics, Diagnostic Approach and Outcome of Thyroid Incidental Findings vs. Clinically Overt Thyroid Nodules: An Observational Single-Centre Study
Tom Jansen, Nike Stikkelbroeck, Annenienke van de Ven, Ilse van Engen-van Grunsven, Marcel Janssen, Han Bonenkamp, Martin Gotthardt, Romana T. Netea-Maier
Cancers.2023; 15(8): 2350. CrossRef - Lower Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Patients Detected by Screening: A Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 69. CrossRef - The 2017 United States Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation for Thyroid Cancer Screening Is No Longer the Gold Standard
Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 72. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Screening: How to Maximize Its Benefits and Minimize Its Harms
Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 75. CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics, Diagnostic Approach and Outcome of Thyroid Incidental Findings vs. Clinically Overt Thyroid Nodules: An Observational Single-Centre Study

- Thyroid
Thyroid Cancer Screening - Lower Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Patients Detected by Screening: A Meta-Analysis
- Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):93-103. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1667
- 2,180 View
- 117 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
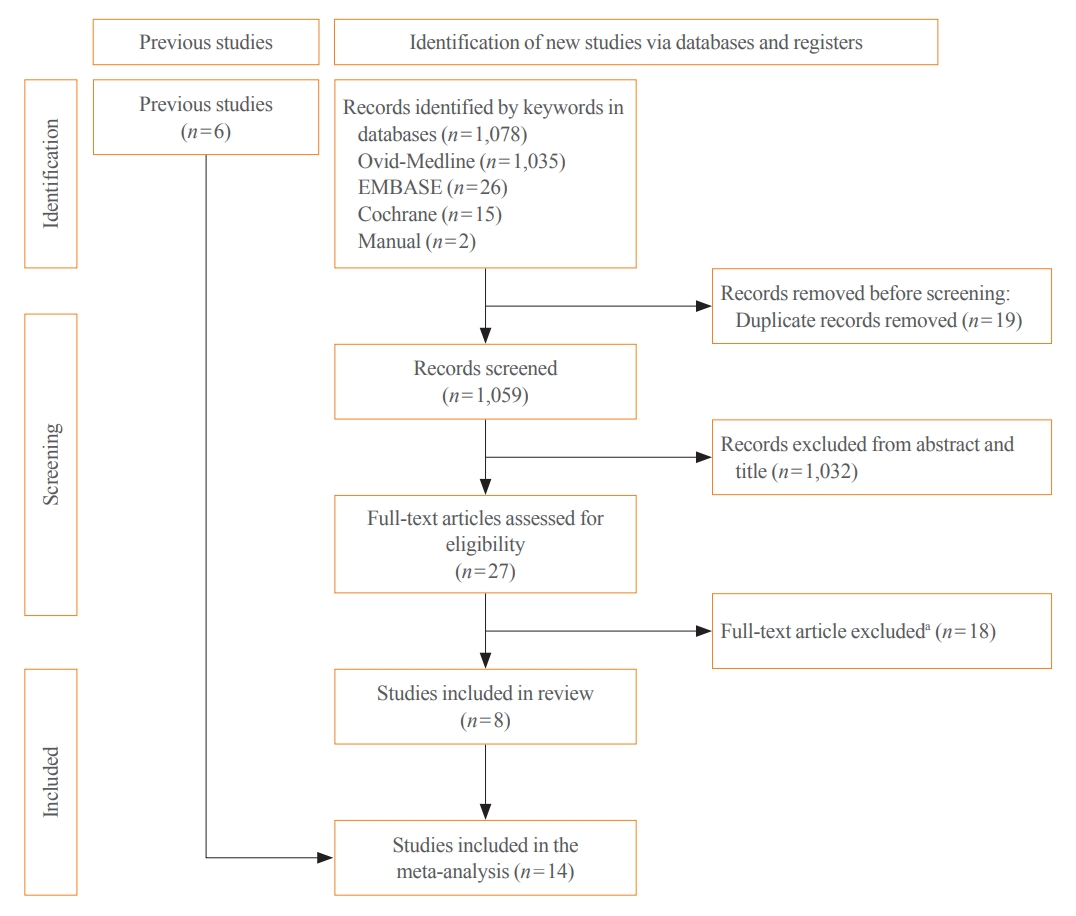
ePub - Background
Thyroid cancer screening has contributed to the skyrocketing prevalence of thyroid cancer. However, the true benefit of thyroid cancer screening is not fully understood. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of screening on the clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer by comparing incidental thyroid cancer (ITC) with non-incidental thyroid cancer (NITC) through a meta-analysis.
Methods
PubMed and Embase were searched from inception to September 2022. We estimated and compared the prevalence of high-risk features (aggressive histology of thyroid cancer, extrathyroidal extension, metastasis to regional lymph nodes or distant organs, and advanced tumor-node-metastasis [TNM] stage), thyroid cancer-specific death, and recurrence in the ITC and NITC groups. We also calculated pooled risks and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the outcomes derived from these two groups.
Results
From 1,078 studies screened, 14 were included. In comparison to NITC, the ITC group had a lower incidence of aggressive histology (odds ratio [OR], 0.46; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.7), smaller tumors (mean difference, −7.9 mm; 95% CI, −10.2 to −5.6), lymph node metastasis (OR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.48 to 0.86), and distant metastasis (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.23 to 0.77). The risks of recurrence and thyroid cancer-specific mortality were also lower in the ITC group (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.71 and OR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.28 to 0.74) than in the NITC group.
Conclusion
Our findings provide important evidence of a survival benefit from the early detection of thyroid cancer compared to symptomatic thyroid cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 69. CrossRef - The 2017 United States Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation for Thyroid Cancer Screening Is No Longer the Gold Standard
Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 72. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Screening: How to Maximize Its Benefits and Minimize Its Harms
Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 75. CrossRef - Delayed Surgery for and Outcomes of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Is the Pendulum Still Swinging?
Giorgio Grani
Clinical Thyroidology.2023; 35(5): 192. CrossRef
- To Screen or Not to Screen?

- Thyroid
- BRAFV600E Mutation Enhances Estrogen-Induced Metastatic Potential of Thyroid Cancer by Regulating the Expression of Estrogen Receptors
- Minjun Kim, Su-jin Kim, Seong Yun Ha, Zhen Xu, Youngjin Han, Hyeon-Gun Jee, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyu Eun Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):879-890. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1563
- 2,787 View
- 215 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
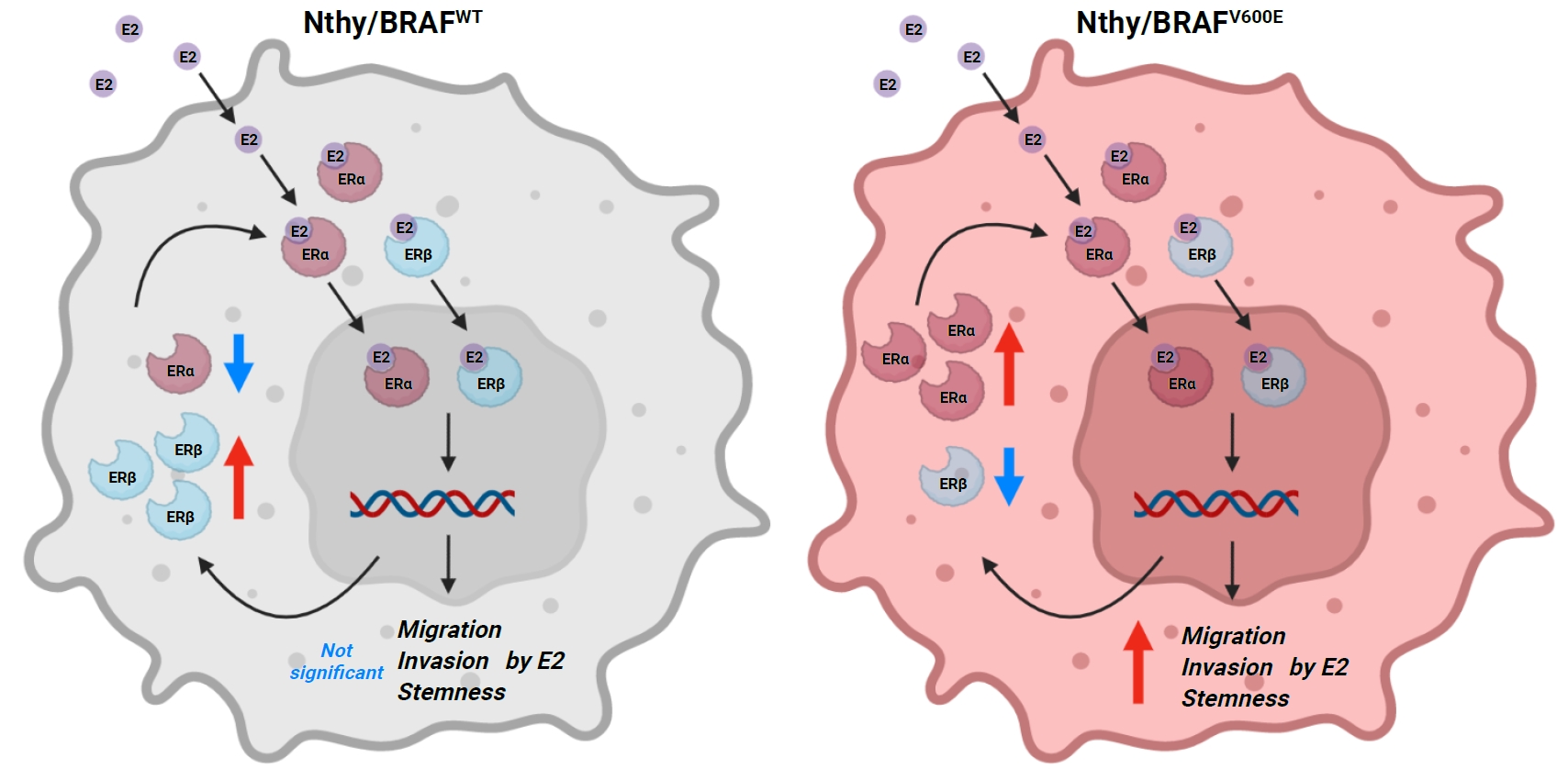
ePub - Background
Cross-talk between mitogen-activated protein kinase and estrogen has been reported; however, the role of BRAFV600E in the estrogen responsiveness of thyroid cancer is unknown. We elucidated the effect of BRAFV600E on the estrogen-induced increase in metastatic potential in thyroid cancer.
Methods
Using a pair of cell lines, human thyroid cell lines which harbor wild type BRAF gene (Nthy/WT) and Nthy/BRAFV600E (Nthy/V600E), the expression of estrogen receptors (ERs) and estrogen-induced metastatic phenotypes were evaluated. Susceptibility to ERα- and ERβ-selective agents was evaluated to confirm differential ER expression. ESR expression was analyzed according to BRAFV600E status and age (≤50 years vs. >50 years) using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data.
Results
Estradiol increased the ERα/ERβ expression ratio in Nthy/V600E, whereas the decreased ERα/ERβ expression ratio was found in Nthy/WT. BRAFV600E-mutated cell lines showed a higher E2-induced increase in metastatic potential, including migration, invasion, and anchorage-independent growth compared with Nthy/WT. An ERα antagonist significantly inhibited migration in Nthy/V600E cells, whereas an ERβ agonist was more effective in Nthy/WT. In the BRAFV600E group, ESR1/ESR2 ratio was significantly higher in younger age group (≤50 years) compared with older age group (>50 years) by TCGA data analysis.
Conclusion
Our data show that BRAFV600E mutation plays a crucial role in the estrogen responsiveness of thyroid cancer by regulating ER expression. Therefore, BRAFV600E might be used as a biomarker when deciding future hormone therapies based on estrogen signaling in thyroid cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy
Kiran Kumar Chitluri, Isaac Arnold Emerson
Heliyon.2024; 10(6): e27655. CrossRef - Three cases of thyroid cancer in transgender female veterans receiving gender-affirming estrogen treatment
John D. Christensen, Hiba T. Basheer
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2024; 15: 100177. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Prevalence, Risk Exposure, and Clinical Features Among Transgender Female Veterans
John David Christensen, Hiba T Basheer, Jose Joaquin Lado Abeal
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of DNA Promoter Methylation and BRAF Mutation in Thyroid Cancer
Farzana Jasmine, Briseis Aschebrook-Kilfoy, Mohammad M. Rahman, Garrett Zaagman, Raymon H. Grogan, Mohammed Kamal, Habibul Ahsan, Muhammad G. Kibriya
Current Oncology.2023; 30(3): 2978. CrossRef - Editorial: Recent advances in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Progression, treatment and survival predictors
Erivelto Martinho Volpi, Margarita Carmen Ramirez-Ortega, Jose Federico Carrillo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy

Letter
- Thyroid
- Re-Increasing Trends in Thyroid Cancer Incidence after a Short Period of Decrease in Korea: Reigniting the Debate on Ultrasound Screening
- Chan Kwon Jung, Ja Seong Bae, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):816-818. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1586

- 1,761 View
- 164 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic total thyroidectomy without isthmectomy: a case report
Hyeji Kim, Hyeonuk Hwang, Hyungju Kwon
The Ewha Medical Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Contents analysis of thyroid cancer-related information uploaded to YouTube by physicians in Korea: endorsing thyroid cancer screening, potentially leading to overdiagnosis
EunKyo Kang, HyoRim Ju, Soojeong Kim, Juyoung Choi
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Survival Comparison of Incidentally Found versus Clinically Detected Thyroid Cancers: An Analysis of a Nationwide Cohort Study
Shinje Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hoonsung Choi, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 81. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: a population-based cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(4): 526. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Active Surveillance Compared to Early Surgery of Small Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Retrospective Study on a Korean Population
Han-Sang Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwangsoon Kim, Jaseong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Sungju Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Chulmin Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic total thyroidectomy without isthmectomy: a case report

Original Article
- Thyroid
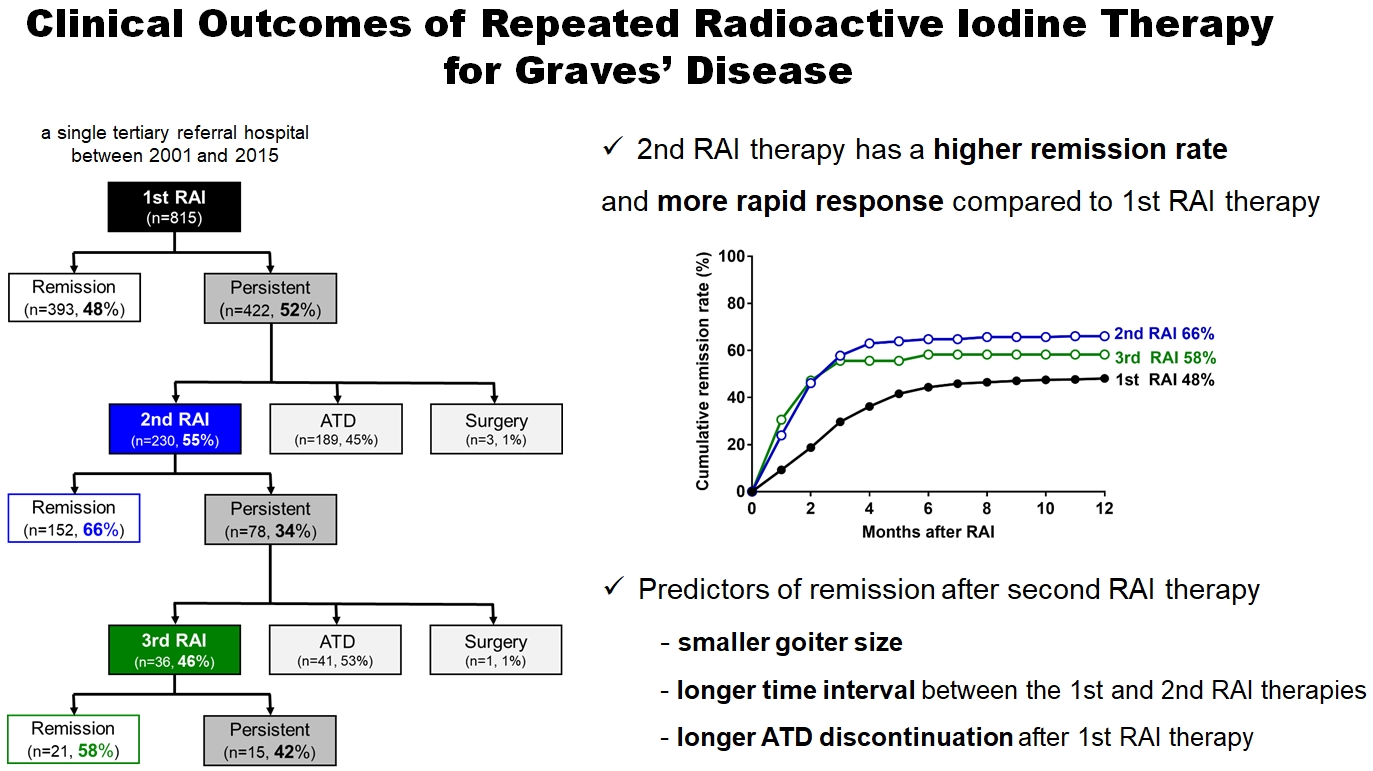
- Clinical Outcomes of Repeated Radioactive Iodine Therapy for Graves’ Disease
- Min Joo Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Ye An Kim, Hoon Sung Choi, Young Joo Park, Do Joon Park, Bo Youn Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):524-532. Published online June 16, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1418
- 4,838 View
- 230 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy is a successful therapeutic modality for Graves’ disease. However, RAI therapy can fail, and RAI therapy after antithyroid drugs (ATDs) has a lower remission rate. Therefore, many patients require repeated RAI therapy. This study investigated the clinical outcomes of repeated RAI therapy for Graves’ disease.
Methods
Patients who underwent RAI therapy as second-line therapy after failure of ATD treatment between 2001 and 2015 were reviewed. Remission was defined as hypothyroid or euthyroid status without ATD, and with or without levothyroxine at 12 months after RAI therapy.
Results
The 1-year remission rate after 2nd RAI therapy (66%, 152/230) is significantly higher than that after 1st RAI therapy (48%, 393/815) or long-term ATD treatment after 1st RAI therapy failure (42%). The clinical response to 2nd RAI therapy was more rapid. The median time intervals from the 2nd RAI therapy to ATD discontinuation (1.3 months) and to the start of levothyroxine replacement (2.5 months) were significantly shorter than those for the 1st RAI therapy. A smaller goiter size, a longer time interval between the 1st and 2nd RAI therapies, and a longer ATD discontinuation period predicted remission after the 2nd RAI therapy. Finally, in 78 patients who failed the 2nd RAI therapy, the mean ATD dosage significantly reduced 5.1 mg over 12 months.
Conclusion
Repeated RAI therapy can be a good therapeutic option, especially in patients with smaller goiters and those who are more responsive to the 1st RAI therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Early Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay over Anti-Thyroid Drug Treatment Could Predict Prognosis of Graves’ Disease
Jin Yu, Han-Sang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Kwanhoon Jo, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Min Hee Kim, Jungmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 338. CrossRef - Effect of liver dysfunction on outcome of radioactive iodine therapy for Graves’ disease
Yuyang Ze, Fei Shao, Xuefeng Feng, Shanmei Shen, Yan Bi, Dalong Zhu, Xiaowen Zhang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Early Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay over Anti-Thyroid Drug Treatment Could Predict Prognosis of Graves’ Disease

Letter
- Thyroid
- Transarterial Radioembolization as an Effective Local Treatment Modality for Liver Metastasis of Thyroid Cancer
- Yoo Hyung Kim, Hyo-Cheol Kim, Yun Bin Lee, Samina Park, Eun-Jae Chung, Jin Chul Paeng, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):383-385. Published online April 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1437
- 2,567 View
- 91 Download

Original Articles
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
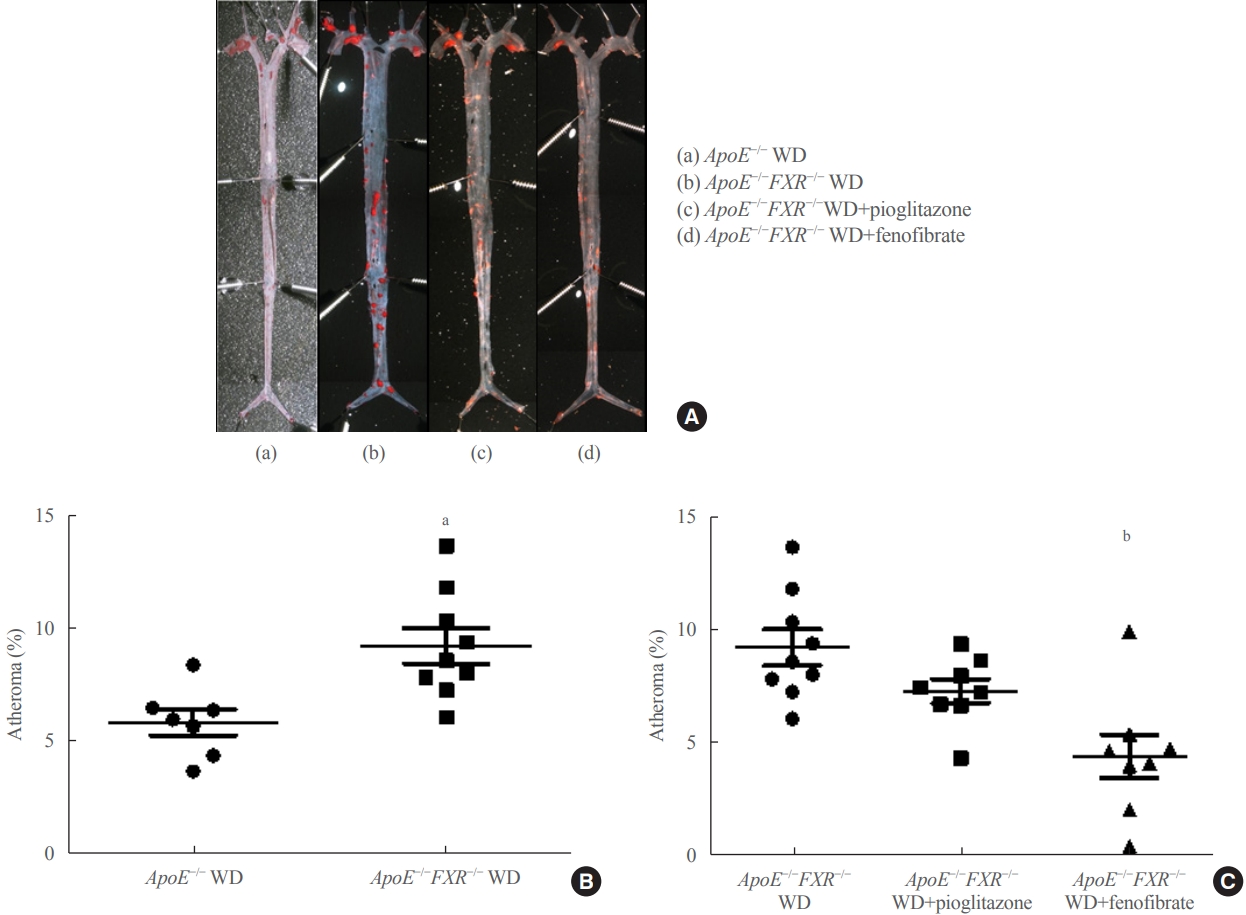
- The Effects of PPAR Agonists on Atherosclerosis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in ApoE−/−FXR−/− Mice
- Yenna Lee, Bo-Rahm Kim, Geun-Hyung Kang, Gwan Jae Lee, Young Joo Park, Haeryoung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1243-1253. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1100
- 5,612 View
- 159 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a bile acid–activated nuclear receptor, is a potent regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism as well as of bile acid metabolism. Previous studies have demonstrated that FXR deficiency is associated with metabolic derangements, including atherosclerosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but its mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of FXR in atherosclerosis and NAFLD and the effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists in mouse models with FXR deficiency.
Methods
En face lipid accumulation analysis, liver histology, serum levels of glucose and lipids, and mRNA expression of genes related to lipid metabolism were compared between apolipoprotein E (ApoE)−/− and ApoE−/−FXR−/− mice. The effects of PPARα and PPARγ agonists were also compared in both groups of mice.
Results
Compared with ApoE−/− mice, ApoE−/−FXR−/− mice showed more severe atherosclerosis, hepatic steatosis, and higher levels of serum cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, accompanied by increased mRNA expression of FAS, ApoC2, TNFα, IL-6 (liver), ATGL, TGH, HSL, and MGL (adipocytes), and decreased mRNA expressions of CPT2 (liver) and Tfam (skeletal muscle). Treatment with a PPARα agonist, but not with a PPARγ agonist, partly reversed atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis, and decreased plasma triglyceride levels in the ApoE−/−FXR−/− mice, in association with increased mRNA expression of CD36 and FATP and decreased expression of ApoC2 and ApoC3 (liver).
Conclusion
Loss of FXR is associated with aggravation of atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis in ApoE-deficient mice, which could be reversed by a PPARα agonist through induction of fatty acid uptake, β-oxidation, and triglyceride hydrolysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the hepatotoxicity of Psoralea corylifolia L. based on a zebrafish model
Shu-Yan Gao, Jing-Cheng Zhao, Qing Xia, Chen Sun, Maimaiti Aili, Ainiwaer Talifu, Shi-Xia Huo, Yun Zhang, Zhi-Jian Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics
Yuxiao Jiang, Lili Wu, Xiaopeng Zhu, Hua Bian, Xin Gao, Mingfeng Xia
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase-II dysfunction: A possible novel mechanism for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in hepatocarcinogenesis
Min Yao, Ping Zhou, Yan-Yan Qin, Li Wang, Deng-Fu Yao
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(12): 1765. CrossRef - Emerging Roles of Gut Microbial Modulation of Bile Acid Composition in the Etiology of Cardiovascular Diseases
Tess Yntema, Debby P. Y. Koonen, Folkert Kuipers
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1850. CrossRef - The interplay between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Alexandra C. Finney, Sandeep Das, Dhananjay Kumar, M. Peyton McKinney, Bishuang Cai, Arif Yurdagul, Oren Rom
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting PPARs for therapy of atherosclerosis: A review
Miao Miao, Xue Wang, Tian Liu, Yan-Jie Li, Wen-Qian Yu, Tong-Mei Yang, Shou-Dong Guo
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 242: 125008. CrossRef - Cabernet sauvignon dry red wine ameliorates atherosclerosis in mice by regulating inflammation and endothelial function, activating AMPK phosphorylation, and modulating gut microbiota
Xinlong Cheng, Xue Han, Liangfu Zhou, Yasai Sun, Qian Zhou, Xuan Lin, Zhe Gao, Jie Wang, Wen Zhao
Food Research International.2023; 169: 112942. CrossRef - Impacts of dietary lipids derived from animal or vegetable sources on healthy rats
Mostafa M Dalal, Gamal M Edrees, Hanaa A Hassan, Mamdouh Abdel-Mogib, Mai Alaa El-Dein
Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2023; 10(1): 618. CrossRef - Whey protein hydrolysate alleviated atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis by regulating lipid metabolism in apoE-/- mice fed a Western diet
Kai Wang, Zixin Fu, Xiaoyi Li, Hui Hong, Xin Zhan, Xiaohong Guo, Yongkang Luo, Yuqing Tan
Food Research International.2022; 157: 111419. CrossRef - Melatonin alleviates PM2.5‐induced glucose metabolism disorder and lipidome alteration by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress
Zhou Du, Junjie Hu, Lisen Lin, Qingqing Liang, Mengqi Sun, Zhiwei Sun, Junchao Duan
Journal of Pineal Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef - The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases
Lu Wang, Shiqi Wang, Qing Zhang, Chengqi He, Chenying Fu, Quan Wei
Molecular Biomedicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of the hepatotoxicity of Psoralea corylifolia L. based on a zebrafish model

- Thyroid
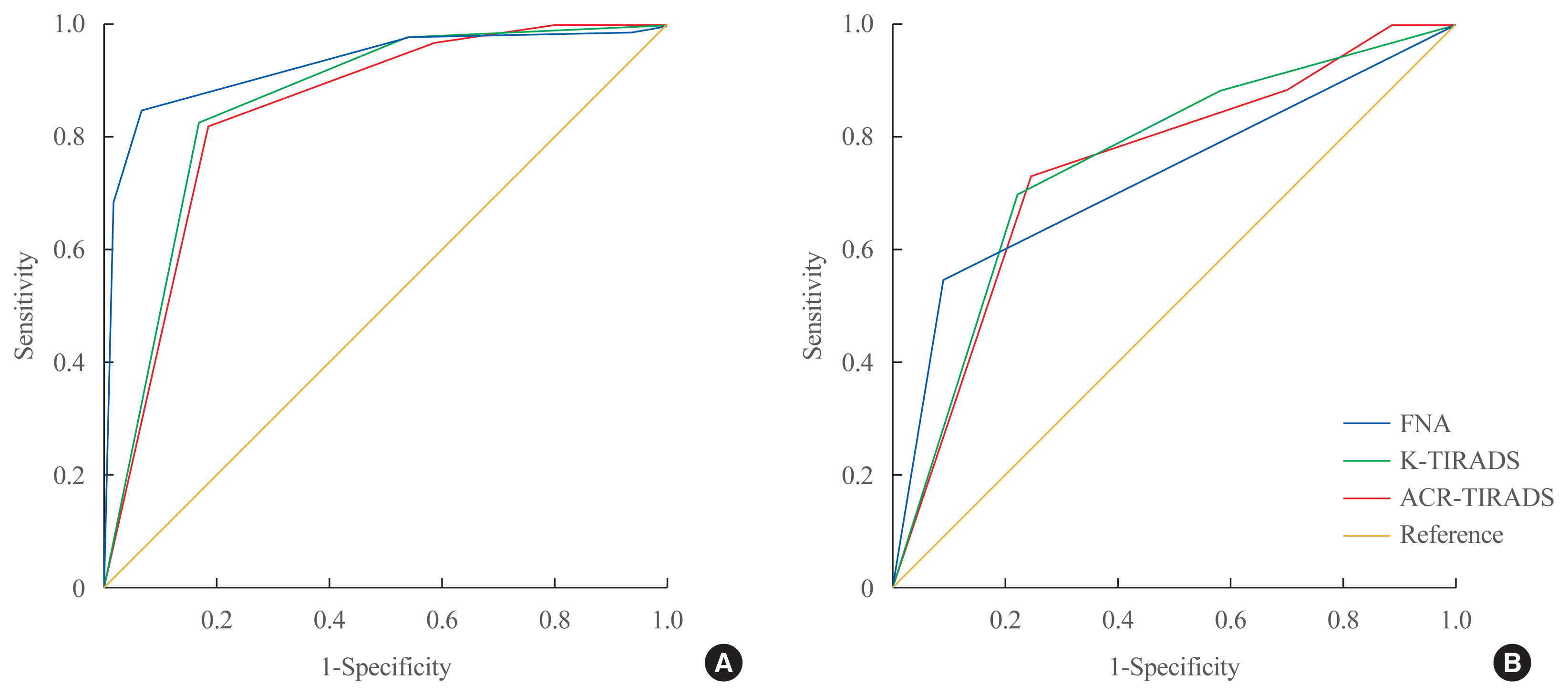
- Comparison of Korean vs. American Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System in Malignancy Risk Assessment of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
- Sunyoung Kang, Seul Ki Kwon, Hoon Sung Choi, Min Joo Kim, Young Joo Park, Do Joon Park, Sun Wook Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1111-1120. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1208
- 3,997 View
- 127 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The management of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules is challenging for clinicians. This study aimed to compare the diagnostic performance of the Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems (K-TIRADS) with that of the American College of Radiology (ACR)-TIRADS for predicting the malignancy risk of indeterminate thyroid nodules.
Methods
Thyroid nodules diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration (FNA) followed by surgery or core needle biopsy at a single referral hospital were enrolled.
Results
Among 200 thyroid nodules, 78 (39.0%) nodules were classified as indeterminate by FNA (Bethesda category III, IV, and V), and 114 (57.0%) nodules were finally diagnosed as malignancy by surgery or core needle biopsy. The area under the curve (AUC) was higher for FNA than for either TIRADS system in all nodules, while all three methods showed similar AUCs for indeterminate nodules. However, for Bethesda category III nodules, applying K-TIRADS 5 significantly increased the risk of malignancy compared to a cytological examination alone (50.0% vs. 26.5%, P=0.028), whereas applying ACR-TIRADS did not lead to a change.
Conclusion
K-TIRADS and ACR-TIRADS showed similar diagnostic performance in assessing indeterminate thyroid nodules, and K-TIRADS had beneficial effects for malignancy prediction in Bethesda category III nodules. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is the nodule location a predictive risk factor for cancer in AUS/FLUS thyroid nodules? A retrospective cohort study
Saad M. Alqahtani, Bassam A. Altalhi, Yousef S. Alalawi, Saif S. Al-Sobhi
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Various Ultrasound Risk Stratification Systems for Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: A Meta-Analysis
Ji-Sun Kim, Byung Guk Kim, Gulnaz Stybayeva, Se Hwan Hwang
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 424. CrossRef - The impact of thyroid imaging reporting and data system on the management of Bethesda III thyroid nodules
Saad M. Alqahtani, Saif S. Al-Sobhi, Mohammed A. Alturiqy, Riyadh I. Alsalloum, Hindi N. Al-Hindi
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2023; 18(3): 506. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Six Ultrasound Risk Stratification Systems for Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Do Hyun Kim, Sung Won Kim, Mohammed Abdullah Basurrah, Jueun Lee, Se Hwan Hwang
American Journal of Roentgenology.2023; 220(6): 791. CrossRef - Diagnostic efficiency among Eu-/C-/ACR-TIRADS and S-Detect for thyroid nodules: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Longtao Yang, Cong Li, Zhe Chen, Shaqi He, Zhiyuan Wang, Jun Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of diagnostic performance of two ultrasound risk stratification systems for thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yun Jin Kang, Hee Sun Ahn, Gulnaz Stybayeva, Ju Eun Lee, Se Hwan Hwang
La radiologia medica.2023; 128(11): 1407. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of ACR and Kwak TI-RADS for Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: An Update Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yun Jin Kang, Gulnaz Stybayeya, Ju Eun Lee, Se Hwan Hwang
Cancers.2022; 14(23): 5961. CrossRef - Comparison of Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems in Malignancy Risk Stratification of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules
Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 974. CrossRef
- Is the nodule location a predictive risk factor for cancer in AUS/FLUS thyroid nodules? A retrospective cohort study

- Thyroid
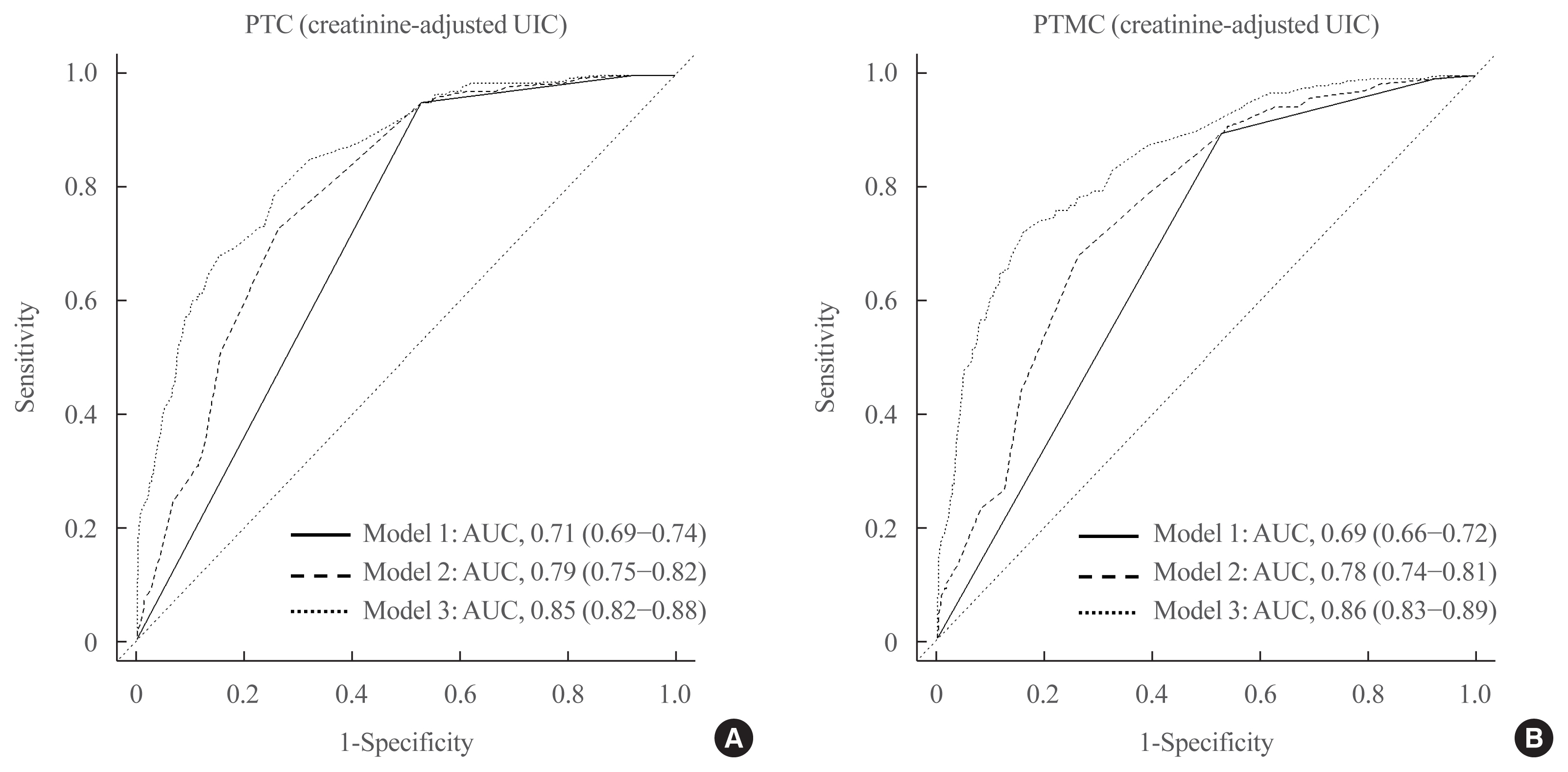
- Association between Iodine Intake, Thyroid Function, and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Case-Control Study
- Kyungsik Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyu Eun Lee, Dong-Wook Lee, Sue K. Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):790-799. Published online August 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1034
- 4,734 View
- 237 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to assess the effects of iodine intake, thyroid function, and their combined effect on the risk of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC).
Methods
A case-control study was conducted including 500 community-based controls who had undergone a health check-up, and 446 overall PTC cases (209 PTC and 237 PTMC) from the Thyroid Cancer Longitudinal Study. Urinary iodine concentration (UIC), was used as an indicator of iodine intake, and serum for thyroid function. The risk of PTC and PTMC was estimated using unconditional logistic regression.
Results
Excessive iodine intake (UIC ≥220 μg/gCr) was associated with both PTC (odds ratio [OR], 18.13 95% confidence interval [CI], 8.87 to 37.04) and PTMC (OR, 8.02; 95% CI, 4.64 to 13.87), compared to adequate iodine intake (UIC, 85 to 219 μg/gCr). Free thyroxine (T4) levels ≥1.25 ng/dL were associated with PTC (OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.36 to 2.87) and PTMC (OR, 2.98; 95% CI, 2.01 to 4.41), compared to free T4 levels of 0.7 to 1.24 ng/dL. Individuals with excessive iodine intake and high free T4 levels had a greatly increased OR of PTC (OR, 43.48; 95% CI, 12.63 to 149.62), and PTMC (OR, 26.96; 95% CI, 10.26 to 70.89), compared to individuals with adequate iodine intake and low free T4 levels.
Conclusion
Excessive iodine intake using creatinine-adjusted UIC and high free T4 levels may have a synergistic effect on PTC and PTMC. Considering both iodine intake and thyroid function is important to assess PTC and PTMC risk. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between urinary iodine concentration and the risk of papillary thyroid cancer by sex and age: a case–control study
Yerin Hwang, Hyun-Kyung Oh, Jae Hoon Chung, Sun Wook Kim, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Myung-Hee Shin
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between iodine nutrition and cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Hengqiang Zhao, Jin Hu, Le Cui, Yiping Gong, Tao Huang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex-specific Associations between Body Mass Index and Thyroid Cancer Incidence among Korean Adults
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Kyungsik Kim, Sangjun Lee, Sue K. Park
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2023; 32(9): 1227. CrossRef - Nomogram Model Based on Iodine Nutrition and Clinical Characteristics of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma to Predict Lateral Lymph Node Metastasis
Junrong Wang, Yuzhang Gao, Yuxuan Zong, Weitong Gao, Xueying Wang, Ji Sun, Susheng Miao
Cancer Control.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Content of Copper, Iron, Iodine, Rubidium, Strontium and Zinc in Thyroid Malignant Nodules and Thyroid Tissue adjacent to Nodules
Vladimir Zaichick, Qiping Dong
Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 1(4): 7. CrossRef - Distinguish Thyroid Malignant from Benign Alterations using Trace Element Contents in Nodular Tissue determined by Neutron Activation and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Vladimir Zaichick
Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 1(4): 18. CrossRef - Seaweed and Iodine Intakes and SLC5A5 rs77277498 in Relation to Thyroid Cancer
Tung Hoang, Eun Kyung Lee, Jeonghee Lee, Yul Hwangbo, Jeongseon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 513. CrossRef - Iodine nutrition and papillary thyroid cancer
Xueqi Zhang, Fan Zhang, Qiuxian Li, Chuyao Feng, Weiping Teng
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between urinary iodine concentration and papillary thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xueqi Zhang, Fan Zhang, Qiuxian Li, Renaguli Aihaiti, Chuyao Feng, Deshi Chen, Xu Zhao, Weiping Teng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening and validation of lymph node metastasis risk-factor genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Qiaoyue Zhang, Jing Li, Hengyan Shen, Xinyu Bai, Tao Zhang, Ping Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis of Thyroid Malignancy using Levels of Chemical Element Contents in Nodular Tissue
Vladimir Zaichick
Journal of Health Care and Research.2022; 3(1): 16. CrossRef - Associations of Habitual Mineral Intake with New-Onset Prediabetes/Diabetes after Acute Pancreatitis
Claire F. Norbitt, Wandia Kimita, Juyeon Ko, Sakina H. Bharmal, Maxim S. Petrov
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 3978. CrossRef
- Association between urinary iodine concentration and the risk of papillary thyroid cancer by sex and age: a case–control study

- Thyroid
- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Recurrence-Free Survival of Rare Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas in Korea: A Retrospective Study
- Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Hwa Young Ahn, Hee Sung Kim, Yong Joon Suh, Dughyun Choi, Bu Kyung Kim, Go Eun Yang, Il-Seok Park, Ka Hee Yi, Chan Kwon Jung, Bo Hyun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):619-627. Published online June 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.974
- 4,696 View
- 180 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate the clinicopathological features and biological behaviors of Korean thyroid cancer patients with rare variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) to address the ambiguity regarding the prognostic consequences of these variants.
Methods
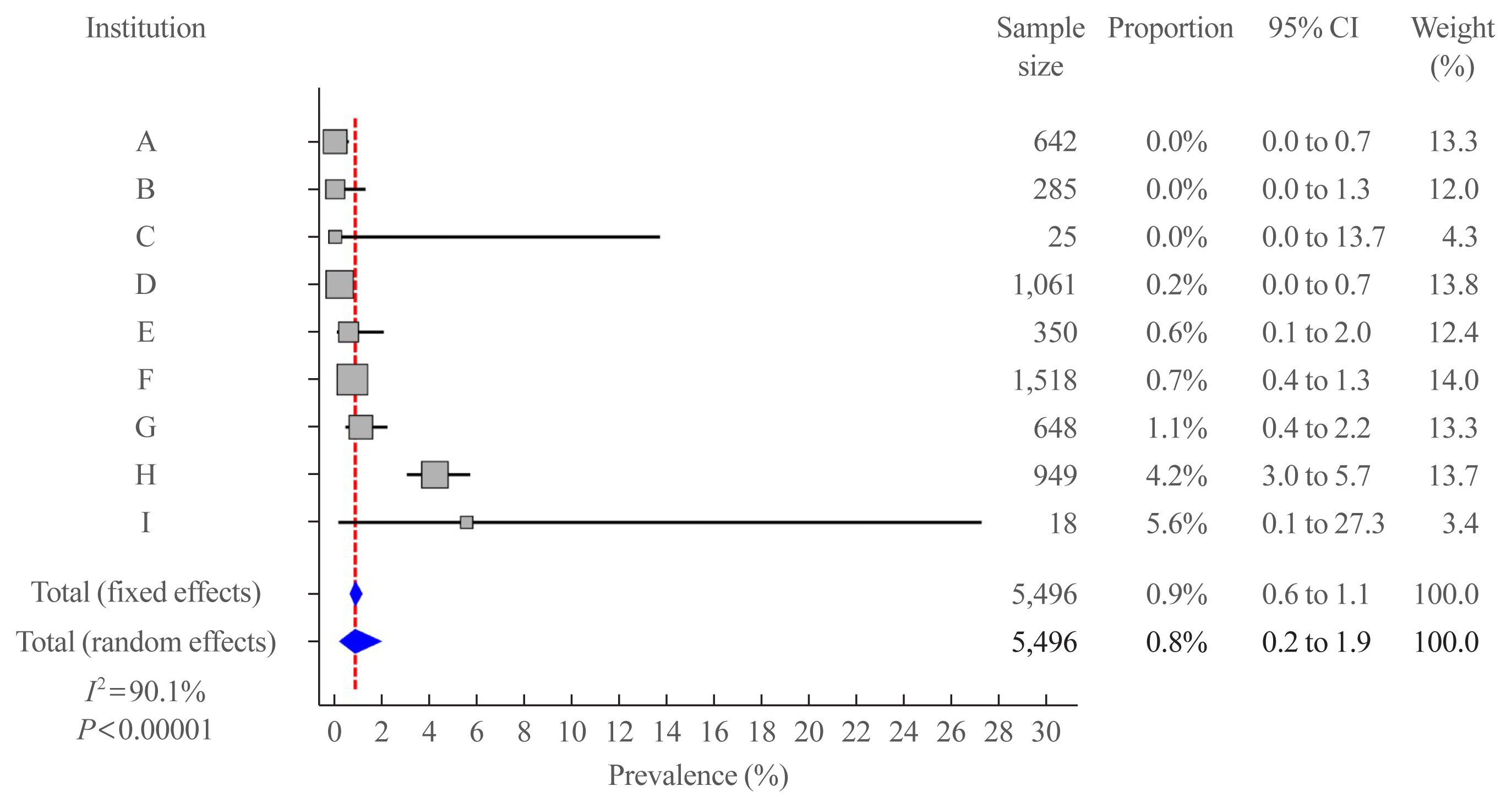
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 5,496 patients who underwent thyroid surgery for PTC, between January and December 2012, in nine tertiary hospitals. Rare PTC variants included tall cell (TCV), columnar cell (CCV), diffuse sclerosing (DSV), cribriform-morular (CMV), solid (SV), hobnail, and Warthin-like variants. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was defined as the time from the date of thyroidectomy until recurrence.
Results
Rare variants accounted for 1.1% (n=63) of the PTC patients; with 0.9% TCV, 0.02% CCV, 0.1% DSV, 0.1% CMV, and 0.1% SV. The mean age of patients and primary tumor size were 42.1±13.1 years and 1.3±0.9 cm, respectively. Extrathyroidal extension and cervical lymph node metastasis were observed in 38 (60.3%) and 37 (58.7%) patients, respectively. Ultrasonographic findings revealed typical malignant features in most cases. During a median follow-up of 7 years, 6.3% of patients experienced a locoregional recurrence. The 5-year RFS rates were 71.4% in patients with DSV or SV, 95.9% for TCV, or CCV, and 100% for other variants. DSV emerged an independent risk factor associated with shorter RFS.
Conclusion
In this multicenter Korean cohort, rare variants accounted for 1.1% of all PTC cases, with TCV being the most frequent subtype. DSV emerged as a significant prognostic factor for RFS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Chae A Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 290. CrossRef - Do Histologically Aggressive Subtypes of Papillary Thyroid
Microcarcinoma have Worse Clinical Outcome than Non-Aggressive Papillary Thyroid
Microcarcinoma Subtypes? A Multicenter Cohort Study
Sayid Shafi Zuhur, Hunkar Aggul, Ugur Avci, Selvinaz Erol, Mazhar Müslüm Tuna, Serhat Uysal, Gulhan Akbaba, Faruk Kilinç, Merve Catak, Sakin Tekin, Ogun Irem Bilen, Beyza Olcay Öztürk, Ecem Bilgehan Erden, Gulsah Elbuken, Halise Cinar Yavuz, Pinar Kadiogl
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(05): 323. CrossRef - The Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinomas: a clinicopathologic analysis report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Yijia Zhang, Pengyu Hao, Mingzhen Zhao, Xingbin Shen
Oncologie.2023; 25(5): 581. CrossRef - A Retrospective Cohort Study with Validation of Predictors of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Outcomes
Ayanthi Wijewardene, Anthony J. Gill, Matti Gild, Diana L. Learoyd, Anthony Robert Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu, Paul Roach, Geoffrey Schembri, Jeremy Hoang, Bruce Robinson, Lyndal Tacon, Roderick Clifton-Bligh
Thyroid.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological Implications of the BRAFV600E Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma of Ukrainian Patients Exposed to the Chernobyl Radiation in Childhood: A Study for 30 Years After the Accident
Liudmyla Zurnadzhy, Tetiana Bogdanova, Tatiana I. Rogounovitch, Masahiro Ito, Mykola Tronko, Shunichi Yamashita, Norisato Mitsutake, Michael Bolgov, Serhii Chernyshov, Sergii Masiuk, Vladimir A. Saenko
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma

- Thyroid
- A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial for Assessing the Usefulness of Suppressing Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Target Levels after Thyroid Lobectomy in Low to Intermediate Risk Thyroid Cancer Patients (MASTER): A Study Protocol
- Eun Kyung Lee, Yea Eun Kang, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Ki-Wook Chung, Eu Jeong Ku, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Eonju Jeon, Se Hyun Paek, Yong Sang Lee, Dong Mee Lim, Yong Joon Suh, Ha Kyoung Park, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Sue K. Park, Eun-Jae Jung, June Young Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Joon Hwa Hong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Young Ki Lee, Hyeong Won Yu, Sujeong Go, Young Mi Kang, MASTER study group
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):574-581. Published online May 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.943
- 6,290 View
- 268 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
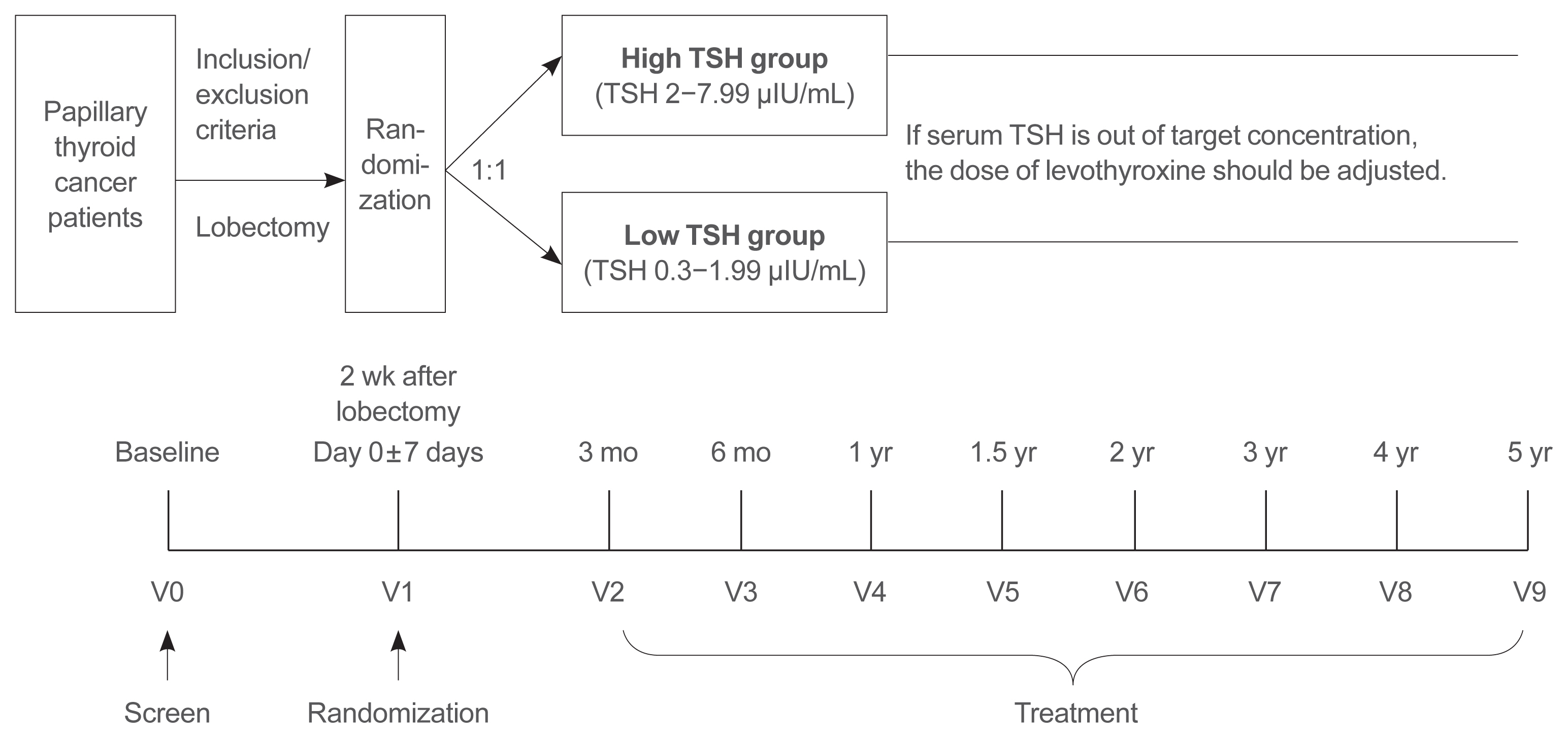
ePub - Background
Postoperative thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) suppression therapy is recommended for patients with intermediate- and high-risk differentiated thyroid cancer to prevent the recurrence of thyroid cancer. With the recent increase in small thyroid cancer cases, the extent of resection during surgery has generally decreased. Therefore, questions have been raised about the efficacy and long-term side effects of TSH suppression therapy in patients who have undergone a lobectomy.
Methods
This is a multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial in which 2,986 patients with papillary thyroid cancer are randomized into a high-TSH group (intervention) and a low-TSH group (control) after having undergone a lobectomy. The principle of treatment includes a TSH-lowering regimen aimed at TSH levels between 0.3 and 1.99 μIU/mL in the low-TSH group. The high-TSH group targets TSH levels between 2.0 and 7.99 μIU/mL. The dose of levothyroxine will be adjusted at each visit to maintain the target TSH level. The primary outcome is recurrence-free survival, as assessed by neck ultrasound every 6 to 12 months. Secondary endpoints include disease-free survival, overall survival, success rate in reaching the TSH target range, the proportion of patients with major cardiovascular diseases or bone metabolic disease, the quality of life, and medical costs. The follow-up period is 5 years.
Conclusion
The results of this trial will contribute to establishing the optimal indication for TSH suppression therapy in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer patients by evaluating the benefit and harm of lowering TSH levels in terms of recurrence, metabolic complications, costs, and quality of life. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression on quality of life in thyroid lobectomy patients: interim analysis of a multicenter, randomized controlled trial in low- to intermediate-risk thyroid cancer patients (MASTER study)
Ja Kyung Lee, Eu Jeong Ku, Su-jin Kim, Woochul Kim, Jae Won Cho, Kyong Yeun Jung, Hyeong Won Yu, Yea Eun Kang, Mijin Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Junsun Ryu, June Young Choi
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2024; 106(1): 19. CrossRef - Clinical impact of coexistent chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis on central lymph node metastasis in low- to intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: The MASTER study
Da Beom Heo, Ho-Ryun Won, Kyung Tae, Yea Eun Kang, Eonju Jeon, Yong Bae Ji, Jae Won Chang, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Eu Jeong Ku, Eun Kyung Lee, Mijin Kim, Jun-Ho Choe, Bon Seok Koo
Surgery.2024; 175(4): 1049. CrossRef - Dynamic Changes in Treatment Response af-ter 131I in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Their Relationship with Recurrence Risk Stratification and TNM Staging
璐 狄
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 1083. CrossRef - ASO Author Reflections: Active Surveillance may be Possible in Patients with T1b Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Over 55 Years of Age Without High-Risk Features on Preoperative Examinations
Ho-Ryun Won, Eonju Jeon, Da Beom Heo, Jae Won Chang, Minho Shong, Je Ryong Kim, Hyemi Ko, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Kyong Hye Joung, Ji Min Kim, Younju Lee, Sung-Woo Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Yong Bae Ji, Kyung Tae, Bon Seok Koo
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(4): 2254. CrossRef - Outcomes and Trends of Treatments in High‐Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Arash Abiri, Khodayar Goshtasbi, Sina J. Torabi, Edward C. Kuan, William B. Armstrong, Tjoson Tjoa, Yarah M. Haidar
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2023; 168(4): 745. CrossRef - Current Controversies in Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Reducing Overtreatment in an Era of Overdiagnosis
Timothy M Ullmann, Maria Papaleontiou, Julie Ann Sosa
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(2): 271. CrossRef - Age-Dependent Clinicopathological Characteristics of Patients with T1b Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Implications for the Possibility of Active Surveillance
Ho-Ryun Won, Eonju Jeon, Da Beom Heo, Jae Won Chang, Minho Shong, Je Ryong Kim, Hyemi Ko, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Kyong Hye Joung, Ji Min Kim, Younju Lee, Sung-Woo Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Yong Bae Ji, Kyung Tae, Bon Seok Koo
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(4): 2246. CrossRef - Potential impact of obesity on the aggressiveness of low- to intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: results from a MASTER cohort study
Mijin Kim, Yae Eun Kang, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Eu Jeong Ku, June Young Choi, Eun Kyung Lee, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrine.2023; 82(1): 134. CrossRef - Differentiated thyroid cancer: a focus on post-operative thyroid hormone replacement and thyrotropin suppression therapy
Benjamin J. Gigliotti, Sina Jasim
Endocrine.2023; 83(2): 251. CrossRef - Thyroid stimulating hormone suppression and recurrence after thyroid lobectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Mi Rye Bae, Sung Hoon Nam, Jong-Lyel Roh, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim
Endocrine.2022; 75(2): 487. CrossRef - The Concept of Economic Evaluation and Its Application in Thyroid Cancer Research
Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Woojin Lim, Bo Hyun Kim, Sue K. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 725. CrossRef
- Effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression on quality of life in thyroid lobectomy patients: interim analysis of a multicenter, randomized controlled trial in low- to intermediate-risk thyroid cancer patients (MASTER study)


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



